Treating Gum Disease
Periodontal disease is an infection of the gums, which gradually leads to the destruction of the support of your natural teeth if not taken care of.
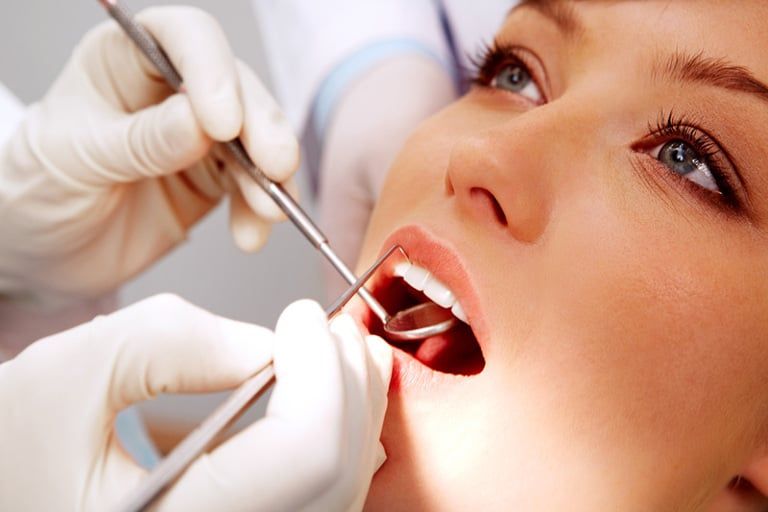
About Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease is an infection of the gums, which gradually leads to the destruction of the support of your natural teeth. This disease affects more than 80% of Americans by the age of 45.
Dental plaque is the primary cause of gum disease. Bacteria found in plaque produce enzymes and toxins which injure the gums. Injured gums turn red, swell and bleed easily.
If this injury is prolonged, the gums separate from the teeth, causing pockets (spaces) to form.
Plaque can also harden into a rough, porous substance known as calculus (tartar).
This can occur both above and below the gum line. As periodontal disease progresses, the supporting gum tissue and bone that holds the teeth in place deteriorate.
If left untreated, this leads to tooth loss. Pain is usually not present until damage from this disease is very advanced.
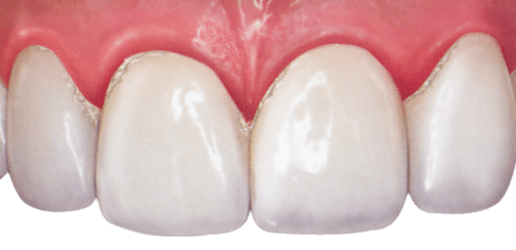
Plaque
Plaque is essentially the start of gum disease problems. Plaque is a build-up from bacteria in the mouth and particles from the foods you eat every day.
Once sugars are introduced to plaque, it turns into a tooth eating acid that sits just above the gum line. If regular oral care isn't standard, the acid will start eating at the teeth producing cavities and the plaque can cause gum disease.
Plaque that is allowed to sit for a prolonged period of time can cause cavities, gingivitis, and other problems in your mouth. If it's left longer than that, serious dental procedures may be required to restore your decaying smile.
Stages Of Gum Disease
Gingivitis is an early stage of gum disease. Gingivitis develops as toxins, enzymes and other plaque byproducts by irritating the gums, making them tender, swollen and likely to bleed easily. Gingivitis generally can be stopped with proper oral hygiene and minor treatment from your dentist. If this is achieved, your gums can return to a healthy state.
Moderate gum disease is when the tooth's bone tissue starts to deteriorate. Periodontitis occurs when plaque byproducts destroy the tissues that anchor your teeth in the bone. The gums deteriorate and begin detaching themselves from the teeth forming gum pockets, which allows more plaque to collect below the gum line. This causes the roots of the teeth to become susceptible to decay. Generally, patients notice an increase in sensitivity to hot and cold and to touch.
Advanced periodontitis occurs when a major amount of gum and bone tissue has been lost and the teeth are losing more and more support due to the loss of periodontal ligament and bone. Some teeth are unable to be saved and must be extracted. If left untreated, advanced periodontitis can cause severe health problems elsewhere in the body.
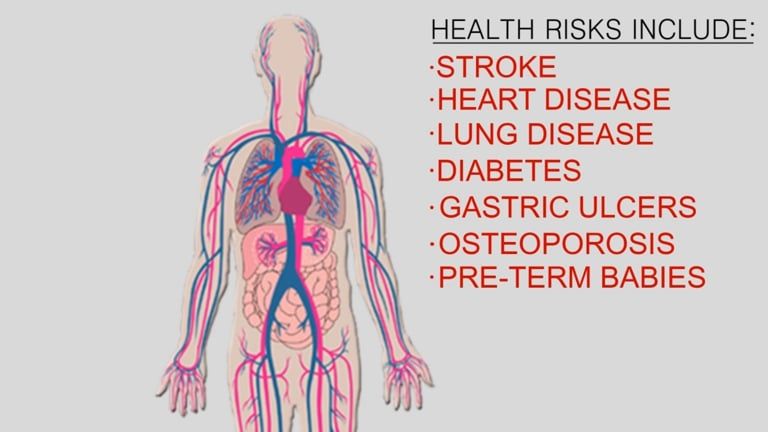
Periodontal Health Effects
Studies have shown links between periodontal (gum) disease, heart disease and other health conditions.
Research further suggests that gum disease may be a more serious risk for heart disease, more so than hypertension, smoking, cholesterol, gender or age.
Researcher's conclusions suggest that bacteria present in infected gums can become loose and move throughout the body through the bloodstream. Once bacteria reaches the arteries, they can irritate them in the same way that they irritate gum tissue causing arterial plaque, which can cause hardening and affect blood-flow.
Sensitivity
Suppress the urge to avoid cleaning teeth that are sensitive to cold! Teeth that have suffered damage from gum disease will always be more sensitive to cold. Avoiding them only makes it worse.
After any dental treatment, teeth may become sensitive. This is their way of letting you know that they've been injured. Any injury (cavity, tooth clenching/grinding, gum infection) can injure the nerves in a tooth. This should not last long if the teeth are kept clean. If the teeth are not kept clean, the sensitivity will remain or get worse.
If your teeth are especially sensitive, consult with your dentist. This could be a sign of the need for root canal treatment, a gum tissue graft, a desensitizing toothpaste (with potassium nitrate), or a concentrated fluoride gel (0.4% stannous- or 1.1% sodium-fluoride) may do the trick.